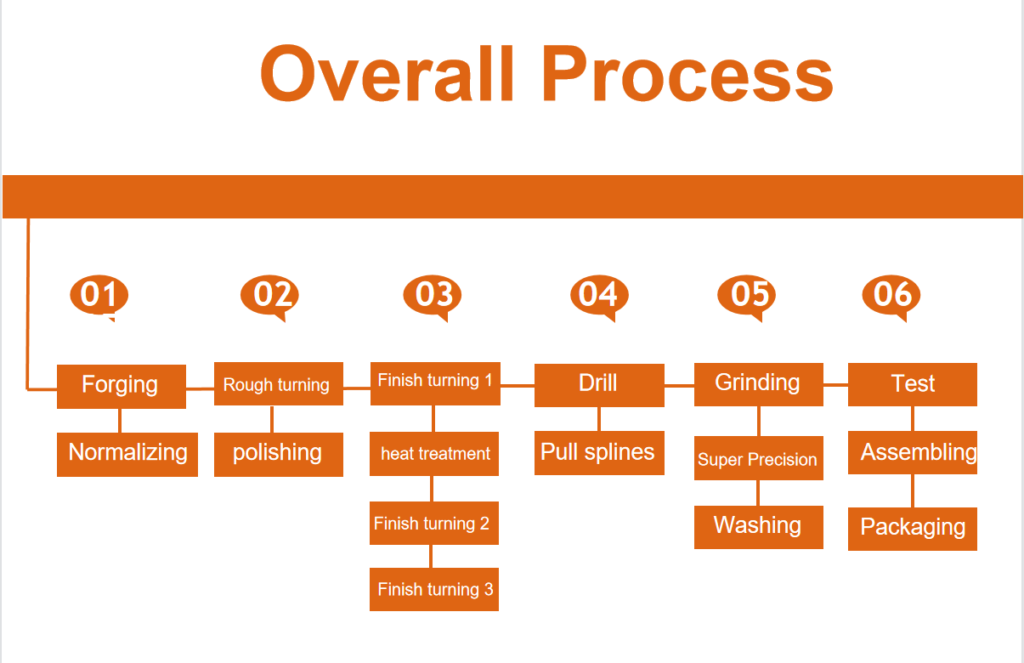
Bearing Manufacturing Process
There are more than 70 complete production steps for a bearing. The main processes and processes are introduced here to help us have a general understanding of the bearing production process.
1.Forging and normalizing:
Forging: Use high-strength materials such as GCR15 and 65MN as raw materials, cut them into a certain length according to the requirements of the parts, heat them, and then use molds for forging.
Normalizing: The forged workpiece is normalized, heated to above 600 degrees, cooled, and kept at 180 to 200 degrees for 3 to 4 hours to stabilize the internal structure, thereby eliminating material stress and improving the mechanical properties of the material.
2.Rough turning and polishing:
Rough turning: remove the oxide scale and allowance on the surface of the workpiece after forging and normalizing to prepare for subsequent fine processing.
Polishing: Polishing the rough-turned workpiece to remove surface burrs, making the surface of the unprocessed parts more beautiful, and also providing a better processing basis for subsequent processes.
3.Finishing and heat treatment:
Finish turning: According to the requirements of the drawing, the workpiece is subjected to multiple finishing turns to obtain precise size and shape.
Heat treatment: Perform heat treatment such as quenching on the workpiece to improve the hardness and wear resistance of the bearing. During the quenching process, the heating temperature, holding time and cooling rate need to be controlled to achieve the ideal hardness and structure.
4.Drilling and drawing splines:
Drill corresponding holes according to the part design drawings, and process matching splines to meet the assembly and use requirements of the bearing.
5.Grinding, superfine and water washing:
Grinding: Grinding the inner and outer rings, raceways, etc. of the bearing through grinding machines and other equipment to improve the accuracy and surface quality of the bearing.
Superfine: Use a grinder and oilstone to further grind the bearing surface to make its roughness meet the requirements.
Water washing: Clean the impurities and oil on the bearing surface to ensure the cleanliness of the bearing. Cleaning methods usually include ultrasonic oil washing, water washing and drying.
6.Testing, assembly and packaging:
Testing: Conduct quality inspection on the processed bearings, including testing of dimensions, hardness, wear resistance and other indicators to ensure that the quality of the bearings meets the requirements.
Assembly: Assemble the various parts of the bearing to form a complete wheel hub bearing.
Packaging: Pack the assembled wheel hub bearings to protect the bearings from damage during transportation and use.
